The Inflation of Higher Education
How far does a university diploma get you? If you imagine you’ll immediately gain a superior position, position, and higher fork out, congratulations. You’ve acquired into the myth.
Larger schooling in The united states is a bubble. There are exceptions, of course. What Large 3 consulting organization can argue with a Harvard MBA? But by and large, the trend is obvious.

This bubble, in accordance to Agora Financial’s Eric Fry, is rooted in a perception:
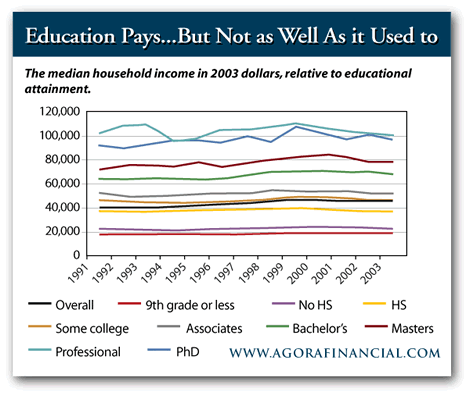
When on a time, a faculty instruction in America was a a person-way ticket to a significant-paying out career and a lofty socio-financial position. Component of its benefit derived from the simple fact that a faculty education was fairly uncommon. In 1950, only about 5% of all Individuals held a bachelor’s diploma.
Since this 5% tended to fare so a great deal improved than the relaxation of the American populace, heaps of individuals commenced to inquire themselves, “Why not ship as lots of youngsters as attainable to faculty?”
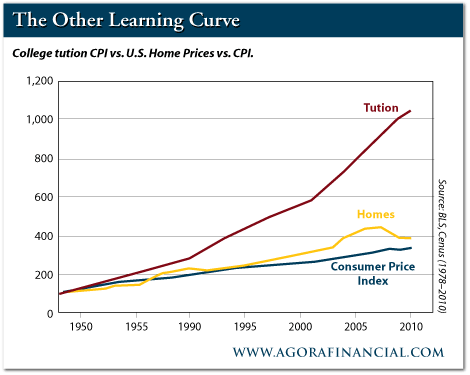
The amount of Individuals with school levels has greater fivefold since 1950, according to Fry. Meanwhile, the quantity people spend for a higher training has “skyrocketed 439 percent given that 1982. Usual source and need simply cannot start to clarify cost increases of this magnitude,” writes to the Washington’s Examiner’s Glenn Harlan Reynolds, quoting an write-up in Money Magazine.
Two issues are behind this increase:
1) Quick Dollars
Sallie Mae, the scholar lending powerhouse in the beginning fashioned as a governing administration-sponsored company in the 1970s, designed it straightforward for students, a lot of with inadequate to no credit history, to get their palms on billions of pounds in federally insured scholar loans.
Fry writes:
In accordance to FinAid.org, the overall amount of money of funds Americans have borrowed on federal government and non-public college student financial loans at $830 billion has surpassed the full American client balance on credit score cards, only $827 billion.
Media studies point out that several of these students do not obviously recognize the terms of their loans. Once they graduate college or university, they’re shocked by greater mortgage payments than they can manage.
But greater training is just one of the most rewarding small business marketplaces in the nation. No university, regardless of whether federal government-operate, non-income or personal, advantages from training learners how to decide on an very affordable diploma in advance of they really go out and get a single.
For instance, there is no point to spending $100,000 on a Harvard diploma in, say, social work if your companies a) do not treatment exactly where your Masters is basically from, and b) your wage will only go as high as $40,000 for each year. College students need to normally make sure the math provides up ahead of receiving a degree. But that is not some thing openly promoted in the market. And why would it be?
The belief that a college education automatically gets you a increased-earning career also “spawned myriad scholarship courses (and) a faculty-development boom,” writes Fry:
Were being it not for Sallie Mae, aspiring faculty graduates could by no means have borrowed much more income than they could ever hope to repay universities could in no way have started to think that they are worth what they cost professors could never have acquired their coddled existence and the price of a higher education instruction could hardly ever have appreciated perfectly outside of any link to its legitimate economic benefit.
Regardless of this, universities perpetuate the perception that each and every diploma they offer you is equally valuable.
2) A Proliferation of Faculties
On the web universities, in particular for-profit types, have proliferated in new a long time. Non-traditional students–stay-at-property parents, persons seeking a second career, learners who really don’t qualify for regular universities, etc.–find on-line universities primarily compelling. They comprise an inflow of persons obtaining degrees.
For-income schools run beneath one rule of thumb: He who marketplaces the most difficult, will get the most business enterprise. Initiatives assortment from recruiters’ payment being tied to enrollment quantities to a relentless affiliate on the internet marketing and advertising effort and hard work (Google “on the web colleges” and you are going to see what I suggest).
For-income also prevent failing students. They want to keep their shoppers delighted. In numerous conditions, college students pay out a ton of money (or consider on a great deal of financial debt) for their levels. They be expecting to move. It’s not in the school’s best fascination to fail pupils, or even give them marginal grades.
However issuing levels to incompetent students devalues levels in general. If anyone can get a degree, what particularly does it confirm? As the share of the workforce with college or university levels has gone up, degrees, with some exceptions, have develop into significantly less beneficial.
Certainly, in accordance to this AZ Central write-up:
Nationally, for-financial gain schools had the highest share of defaults in the United States in 2007: 11 p.c. Group faculties had a nearly 10 per cent price, and personal, non-earnings universities experienced the most affordable rates, at 3.7 %, in accordance to the U.S. Office of Training.
University officials say for-financial gain schools provide an significant role. Like local community schools, they have much more-lenient admission requirements and catch the attention of bigger percentages of learners in financial want: decrease-profits, minorities and more mature than 25. Officers say this explains why a lot more learners wrestle with repaying college student financial loans.
In other words and phrases, the for-revenue procedure has attracted numerous students who can’t find the money for their training, but get levels anyway.
What’s the Real Worth of a Diploma?
The Washington Examiner’s Glenn Reynolds states there are threes ways a higher education education and learning can enable people today make additional cash:
Initial, it may perhaps basically make them much more economically successful by training them techniques valued in the place of work: Personal computer programming, nursing or engineering, say.
2nd, it may deliver a credential that companies want, not since it signifies precise skills, but because it is a weeding instrument that doesn’t deliver civil-rights satisfies as, say, IQ exams may possibly. A four-year school degree, even if its holder acquired no actual expertise, at the very least indicates some ability to present up on time and conduct as instructed.
And, third, a university diploma — at minimum an elite 1 — might hook its holder up with a beneficial social community that can present careers and possibilities in the potential.
Whilst an particular person may rationally pursue all a few of these, only the to start with a single — precise extra techniques — generates a web benefit for society. The other two are just distributional — about who gets the goodies, not about earning more of them.
But lots of universities, especially for-gain ones, never want you to know that.







